In 2018 over 20,000 new homes projects across the US and Canada were designed as “ready for zero” or “zero energy” homes. That means they were designed to be highly energy efficient and ready to produce most of their energy needs through renewable energy. These homes, many of which will be certified through the Department of Energy’s Zero Energy Ready Homes program, use a combination of building design principles and technologically advanced systems to get there. On the way to delivering near-zero energy bills, many of these same features also offer greater comfort, resiliency, and indoor environmental health.
Here are some reasons to build your new Deltec Home as a Zero Energy Ready Home:
- Award-winning certified Zero Energy Ready Homes built in 2019 will save their owners an average of $92,675 in the first 30 years.
- Right now, Deltec clients and their builders who use this program are eligible for an attractive rebate from us. It’s our way of thanking you for your efforts and supporting the growth of worthwhile certification programs.
- A dream home is only built once. Why not build it the smartest way possible?
What Makes a Zero Energy Ready Home Stand Out?
Local building code requirements for energy efficiency, as well as various green building programs which award practices that go above and beyond them, can be a confusing landscape to navigate. Most homeowners are happy to be achieving any green label at all. But there are differences in the rigor between green programs, and in the end benefits to the homeowner, and these differences are worth considering.
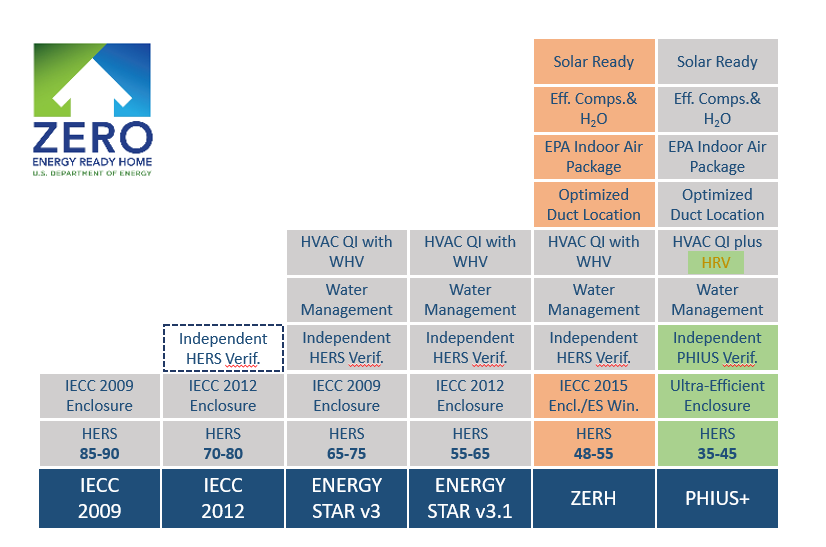
Comparing the high performance features offered by different programs, starting with the IECC 2009 (International Energy Conservation Code) on the left, an older energy code that is still the most common code adopted in the US. Moving right through the 2012 IECC, a newer code with some more stringent requirements, and various versions of the Energy Star for Homes program would provide more performance benefits, including verification by a HERS Rater, water management measures, and HVAC that is quality inspected and includes a whole house ventilation competent. The Zero Energy Ready Home Program (ZERH) adds solar-ready construction, efficient hot water equipment and distribution, indoor air quality requirements, optimized duct location, and IECC 2015 insulation levels at a minimum, to Energy Star base benefits. On the far right, the Passive House Institute US+ Program, PHIUS+, adds to that a requirement for heat recovery ventilation specifically, and even more aggressive insulation and air-tightness measures. The very bottom row shows the typical HERS score a home participating in each program might receive. Image Source: Newport Partners, LLC. Used with permission.
Take the well-known certification, Energy Star for Homes. This program does deliver some great quality assurance benefits, such as an inspection on insulation quality and a requirement for HVAC design and whole house ventilation. But the overall requirements for Energy Star certification are still relatively basic. The program is it as an effective tool for enforcing an adequate job on the same old way of doing things, but it’s not a program that challenging the design of the home itself to perform at a higher level. It takes programs like the Zero Energy Ready Home to really move the industry forward.
One cool thing about ZERH is that it is a science-based standard. Every year the DOE funds research in the building industry to answer common questions that builders and homeowners regularly face when making design choices and selections. Does this practice really save energy, and how much, and does the cost pay itself back over time? What practices have unexpected negative consequences that should be avoided? That knowledge, based on trial and error experience, is fed back into the Zero Energy Ready Home Standard.
How Do I Design my Home to Qualify?
Of course, the details will vary based on the specifics of your home design and on your climate zone, but stepping up to actually completing the certification is not as hard as you think, nor is it often as expensive. ZERH certification is growing among Habitat for Humanity projects just as much as in the custom home market.
Here are the general things you’ll need to do with your home, to be in the realm of certification(1):
- Use approximately 20% higher levels of wall, ceiling, and floor insulation than your local code, and use better performing windows. Deltec can help you with this with our high-R-value wall options and energy efficient window choices.
- Use a higher-efficiency water heating system, such as a heat pump water heater, tankless gas or propane water heater, or solar water heating system.
- Use low-flow water fixtures, design your floor plan so that the water heater is strategically located next to all hot-water using faucets, or install an on-demand recirculating hot water pump to bring hot water to fixtures faster. This has been a popular customer satisfaction feature, as most people hate sending water down the drain while they’re waiting for hot water to arrive.
- Design your floor plan so that 100% of your HVAC equipment and ductwork is inside of the conditioned space—that means it all has to be inside the insulated envelope of your home, not running through the an unheated attic, unheated basement, or the ceiling of an unheated garage. That will enable them to work better and deliver better comfort. While this is common in many Deltecs, pulling this off can be tricky with certain floorplans, such as those with basements that are partially heated and partially unheated, or homes with drive-under garages.
- Use Low-VOC and non-toxic finishes throughout the home, complying with the EPA Indoor Air Plus program. Everything supplied by the Deltec package will comply, but there will be many products that you pick out for your home independent of what comes from our shell package, such as your flooring, your cabinetry, etc, that you will need to pay attention to.
- Install a passive radon mitigation system per EPA guidelines if building in a high radon zone.
- If your build location has enough sun, and if roof or your lot have enough unshaded space to make solar viable, you will need to either install a solar PV system, or rough in a conduit for future solar, or per-create your ground-mount array plans for a future ground-mounted array.
- Before construction begins, Hire a 3rd party HERS Rater certified through the Zero Energy Ready Program to energy model your home, complete a blower door test and duct blaster test, and inspect everything to make sure you’ve followed all of the program requirements. You can find a list of Rater Partners here.
Many of the homeowners that I work with are already interested in some of all of these things. The ZERH is as great framework for putting them all together.
Note (1): Of course this isn’t fully explaining everything you’ll need to do. You have to go read the program documents for that.